Questa categoria
di supernovae
produce un picco
notevole di
luminosità, che
si presenta
pressoché simile
in tutte le
esplosioni di
questo tipo a
causa della
relativa
uniformità delle
masse delle nane
bianche che
esplodono in
seguito ai
processi di
accrescimento.
Per tale ragione
le supernovae di
tipo Ia sono
spesso
utilizzate come
candele standard
per misurare la
distanza della
loro galassia
ospitante,in
quanto la loro
magnitudine
apparente
dipende quasi
esclusivamente
dalla distanza a
cui si trovano.Un
evento del
genere in una
galassia così
vicina
costituisce
un caso raro
e quanto mai
interessante per
la ricerca in
astrofisica,in
quanto
l’osservazione
spettroscopica
ad alta
risoluzione
della Supernova
con
telescopi
professionali,
ci permetterà di
studiare
l’interazione
tra il mezzo
interstellare
distribuito
attorno alla
stella
progenitrice e
l’intenso campo
di radiazione
prodotto
dall’esplosione
e gli ejecta
espulsi dalla
Supernova".Ancora
una volta quindi
la Spettroscopia
fa da padrona e
da metodo
d'indagine
fondamentale per
comprendere la
nascita e
l'evoluzione di
eventi stellari
catastrofici.La
Galassia Sigaro
(nota anche come
M 82 o NGC
3034) è una
galassia attiva
nella
costellazione
dell'Orsa
Maggiore; si
trova a circa 12
milioni di anni
luce ed è
associata alla
più grande e
famosa M81. Si
tratta di un
ottimo esempio
di galassia
starburst,
ovvero con
notevolissimi
eventi di
formazione
stellare.

Un'immagine
LRGB di M81
ottenuta da
Fulvio Mete dal
suo Osservatorio
di Ponte di Nona
a Roma
A close LRGB
image of the
Galaxy by Fulvio
Mete

Un'immagine
recente di
repertorio di
M81 con evidente
la supernova
A recent image
of the galaxy
with the SN
La supernova,
come si è detto,
è stata
classificata di
tipo 1 A sulla
base del suo
spettro che,
alla data del 23
gennaio 2014
presentava ,
come componenti
più evidenti le
righe in
assorbimento del
sodio
NaI D
dovute
all'assorbimento
interstellare e
quelle del
Silicio
ionizzato
Si II a
5468, 5972 e,
principalmente ,
quella a
6355 A,
sul cui
blueshift in
assorbimento
(riga P cygni)
era stata
misurata dagli
Osservatori
professionali una
velocità radiale
di
14.100 Kms il 23
gennaio;
13.400 il 25
gennaio e 12600
il 28 dello
stesso mese,
configurando un
rallentamento
dell'espansione
della shell
di ca 300 Kms al
giorno.
Le Osservazioni
The Observations
Osservazione del
25 gennaio 2014
da Roma:
Celestron 14,
camera CCD Sbig
ST8 XME,
Star Analyser 100
Observation of
january,25, 2014
from Rome,
Italy: Celestron 14,
camera CCD Sbig
ST8 XME,
Star Analyser 100
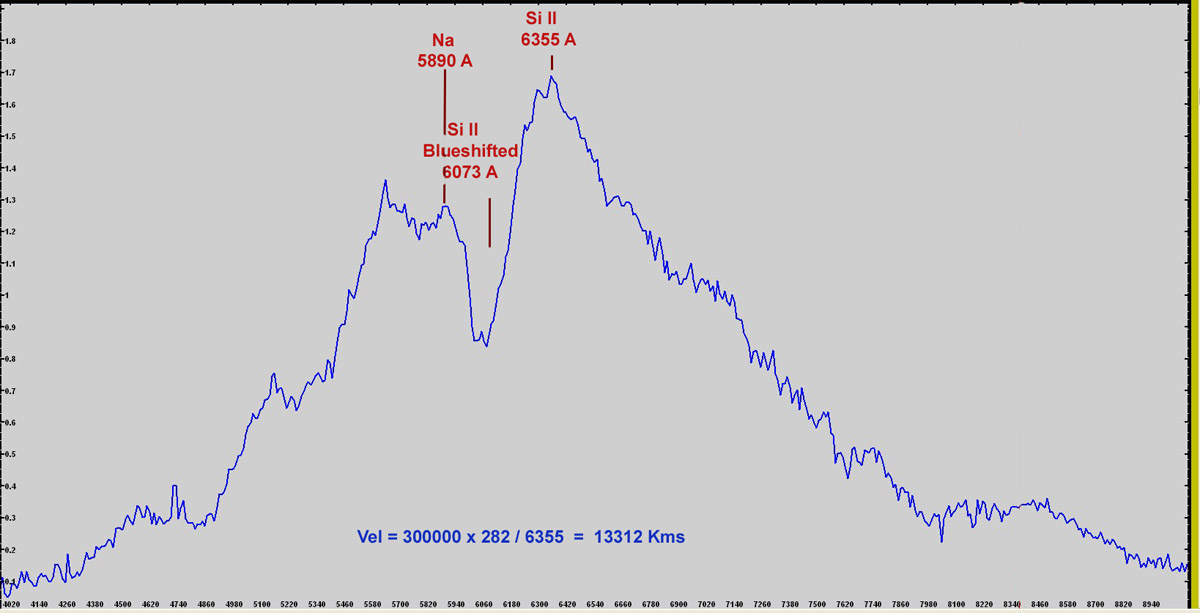
Il profilo è
corretto solo in
lunghezza
d'onda: è
interessante
notare come il
valore della
velocità dell'Si II a 6355 A ,
stimato in
13.312 kms si
discosta
soltanto di 88
kms dal valore
riscontrato da
Osservazioni
professionali,
di 13400 Kms.
The profile is
corrected only
in wavelenght:
it is
interesting to
note as the
value of radial
speed of the
shell of Si II,
calculated in
13.312 Km/sec is
different for
only 88 Km/sec
from that
obtained by
professional, of
13.400 Km/sec
for the same
day.
Osservazione del
6 febbraio 2014
, stesso setup:
Observations of
february, 6,
2014, same setup

Il profilo è
corretto solo in
lunghezza d'onda
:la riga del Si
II in
assorbimento
viene trovata a
6120 A, per una
V di 11093 Kms l
The profile,
corrected only
in wavelenght,
shows a blue
shift of Si II
line at 6120 A,
for a radial
speed of 11093
Km/sec
Osservazione del
28 marzo 2014
da Roma: Celestron 14,
camera CCD Sbig
ST8 XME,
Star Analyser 200
Observation of
march, 28, 2014,
from Rome,Celestron 14,
camera CCD Sbig
ST8 XME,
Star Analyser 200
